Student Extras
Teacher's Guides
The Physics Classroom » Physics Tutorial » Newton's Laws » Newton's Second Law
Newton's Laws - Lesson 3 - Newton's Second Law of Motion
- Newton's Second Law
- The Big Misconception
- Finding Acceleration
- Finding Individual Force Values
- Free Fall and Air Resistance
- Two-Body Problems
Newton's first law of motion predicts the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are balanced. The first law - sometimes referred to as the law of inertia - states that if the forces acting upon an object are balanced, then the acceleration of that object will be 0 m/s/s. Objects at equilibrium (the condition in which all forces balance) will not accelerate. According to Newton, an object will only accelerate if there is a net or unbalanced force acting upon it. The presence of an unbalanced force will accelerate an object - changing its speed, its direction, or both its speed and direction. Newton's second law of motion pertains to the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are not balanced. The second law states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables - the net force acting upon the object and the mass of the object. The acceleration of an object depends directly upon the net force acting upon the object, and inversely upon the mass of the object. As the force acting upon an object is increased, the acceleration of the object is increased. As the mass of an object is increased, the acceleration of the object is decreased. Newton's second law of motion can be formally stated as follows: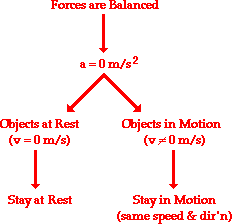

The BIG Equation
The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
This verbal statement can be expressed in equation form as follows:
The above equation is often rearranged to a more familiar form as shown below. The net force is equated to the product of the mass times the acceleration.
 In this entire discussion, the emphasis has been on the net force. The acceleration is directly proportional to the net force; the net force equals mass times acceleration; the acceleration in the same direction as the net force; an acceleration is produced by a net force. The NET FORCE. It is important to remember this distinction. Do not use the value of merely "any 'ole force" in the above equation. It is the net force that is related to acceleration. As discussed in an earlier lesson, the net force is the vector sum of all the forces. If all the individual forces acting upon an object are known, then the net force can be determined. If necessary, review this principle by returning to the practice questions in Lesson 2.
In this entire discussion, the emphasis has been on the net force. The acceleration is directly proportional to the net force; the net force equals mass times acceleration; the acceleration in the same direction as the net force; an acceleration is produced by a net force. The NET FORCE. It is important to remember this distinction. Do not use the value of merely "any 'ole force" in the above equation. It is the net force that is related to acceleration. As discussed in an earlier lesson, the net force is the vector sum of all the forces. If all the individual forces acting upon an object are known, then the net force can be determined. If necessary, review this principle by returning to the practice questions in Lesson 2.
Consistent with the above equation, a unit of force is equal to a unit of mass times a unit of acceleration. By substituting standard metric units for force, mass, and acceleration into the above equation, the following unit equivalency can be written.
The definition of the standard metric unit of force is stated by the above equation. One Newton is defined as the amount of force required to give a 1-kg mass an acceleration of 1 m/s/s.
Your Turn to Practice
 The Fnet = m •a equation is often used in algebraic problem solving. The table below can be filled by substituting into the equation and solving for the unknown quantity. Try it yourself and then use the click on the buttons to view the answers.
The Fnet = m •a equation is often used in algebraic problem solving. The table below can be filled by substituting into the equation and solving for the unknown quantity. Try it yourself and then use the click on the buttons to view the answers.
See Answer Answer: a = 5 m/s/s a = (10 N) / (2 kg) a = 5 m/s/s | |||
See Answer Answer: a = 10 m/s/s a = (20 N) / (2 kg) a = 10 m/s/s | |||
See Answer Answer: a = 5 m/s/s a = (20 N) / (4 kg) a = 5 m/s/s | |||
See Answer Answer: Fnet = 10 N Fnet = (2 kg) • (5 m/s/s) Fnet = 10 N | |||
See Answer Answer: m = 1 kg m = (10 N) / (10 m/s/s) m = 1 kg |
Newton's Second Law as a Guide to Thinking
The numerical information in the table above demonstrates some important qualitative relationships between force, mass, and acceleration. Comparing the values in rows 1 and 2, it can be seen that a doubling of the net force results in a doubling of the acceleration (if mass is held constant). Similarly, comparing the values in rows 2 and 4 demonstrates that a halving of the net force results in a halving of the acceleration (if mass is held constant). Acceleration is directly proportional to net force.
Furthermore, the qualitative relationship between mass and acceleration can be seen by a comparison of the numerical values in the above table. Observe from rows 2 and 3 that a doubling of the mass results in a halving of the acceleration (if force is held constant). And similarly, rows 4 and 5 show that a halving of the mass results in a doubling of the acceleration (if force is held constant). Acceleration is inversely proportional to mass.
The analysis of the table data illustrates that an equation such as Fnet = m*a can be a guide to thinking about how a variation in one quantity might affect another quantity. Whatever alteration is made of the net force, the same change will occur with the acceleration. Double, triple or quadruple the net force, and the acceleration will do the same. On the other hand, whatever alteration is made of the mass, the opposite or inverse change will occur with the acceleration. Double, triple or quadruple the mass, and the acceleration will be one-half, one-third or one-fourth its original value.
The Direction of the Net Force and Acceleration
 As stated above, the direction of the net force is in the same direction as the acceleration. Thus, if the direction of the acceleration is known, then the direction of the net force is also known. Consider the two oil drop diagrams below for an acceleration of a car. From the diagram, determine the direction of the net force that is acting upon the car. Then click the buttons to view the answers. (If necessary, review acceleration from the previous unit.)
As stated above, the direction of the net force is in the same direction as the acceleration. Thus, if the direction of the acceleration is known, then the direction of the net force is also known. Consider the two oil drop diagrams below for an acceleration of a car. From the diagram, determine the direction of the net force that is acting upon the car. Then click the buttons to view the answers. (If necessary, review acceleration from the previous unit.)

See Answer The net force is to the right since the acceleration is to the right. An object which moves to the right and speeds up has a rightward acceleration.

See Answer The net force is to the left since the acceleration is to the left. An object which moves to the right and slows down has a leftward acceleration.
In conclusion, Newton's second law provides the explanation for the behavior of objects upon which the forces do not balance. The law states that unbalanced forces cause objects to accelerate with an acceleration that is directly proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the mass.
We Would Like to Suggest ...
 Sometimes it isn't enough to just read about it. You have to interact with it! And that's exactly what you do when you use one of The Physics Classroom's Interactives. We would like to suggest that you combine the reading of this page with the use of our ForceInteractive. You can find it in the Physics Interactives section of our website. TheForceInteractiveallows a learner to explore the effect of variations in applied force, net force, mass, and friction upon the acceleration of an object.
Sometimes it isn't enough to just read about it. You have to interact with it! And that's exactly what you do when you use one of The Physics Classroom's Interactives. We would like to suggest that you combine the reading of this page with the use of our ForceInteractive. You can find it in the Physics Interactives section of our website. TheForceInteractiveallows a learner to explore the effect of variations in applied force, net force, mass, and friction upon the acceleration of an object.
Visit: Force
Rocket Science!
NASA rockets (and others) accelerate upward off the launch pad as they burn a tremendous amount of fuel. As the fuel is burned and exhausted to propel the rocket, the mass of the rocket changes. As such, the same propulsion force can result in increasing acceleration values over time. Use the Rocket Science widget below to explore this effect.| Rocket Science | ||
|---|---|---|
Check Your Understanding
1. Determine the accelerations that result when a 12-N net force is applied to a 3-kg object and then to a 6-kg object.
See Answer A 3-kg object experiences an acceleration of 4 m/s/s. A 6-kg object experiences an acceleration of 2 m/s/s.
2. A net force of 15 N is exerted on an encyclopedia to cause it to accelerate at a rate of 5 m/s2. Determine the mass of the encyclopedia.
See Answer Use Fnet= m * a with Fnet = 15 N and a = 5 m/s/s. So (15 N) = (m)*(5 m/s/s) And m = 3.0 kg
3. Suppose that a sled is accelerating at a rate of 2 m/s2. If the net force is tripled and the mass is doubled, then what is the new acceleration of the sled?
See Answer Answer: 3 m/s/s The original value of 2 m/s/s must be multiplied by 3 (since a and F are directly proportional) and divided by 2 (since a and m are inversely proportional)
4. Suppose that a sled is accelerating at a rate of 2 m/s2. If the net force is tripled and the mass is halved, then what is the new acceleration of the sled?
See Answer Answer: 12 m/s/s The original value of 2 m/s/s must be multiplied by 3 (since a and F are directly proportional) and divided by 1/2 (since a and m are inversely proportional)
Next Section: Jump To Next Lesson:
 - Shopify)